Measuring & Mitigating GHG Emissions
What gets measured gets managed. This truism is critically important for assessing the impact of climate-polluting emissions. Measurement lays the foundation for understanding current business-as-usual conditions, establishing effective targets, policies, and regulations for the future, and meaningfully engaging governments, communities, and the private sector as key actors in climate governance.
Developing Powerful Tools to Quantify Emissions
With the rise of environmental reporting requirements, emission measurements are used to determine local and national emissions contributions, drive policy development, ensure compliance with regulations, and more. Over the past decade, Abt’s work with the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has contributed to more accurate and transparent emissions accounting through powerful tools that actors at every level use to effectively measure and manage emissions.
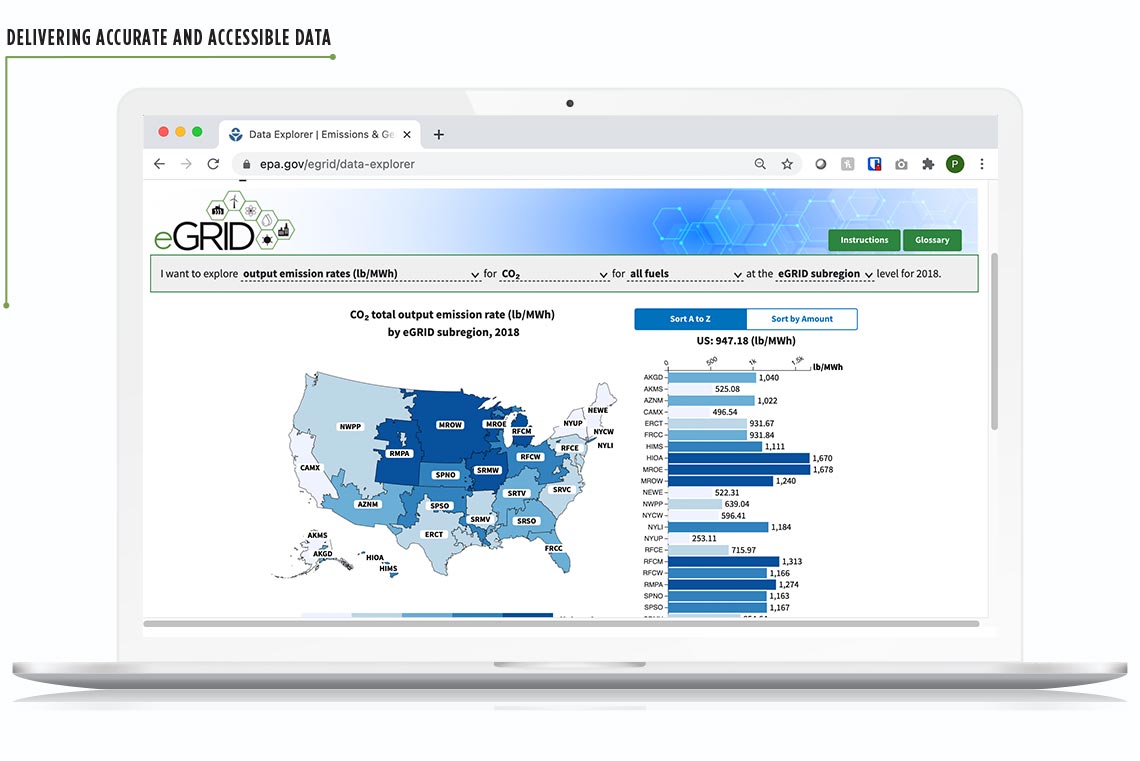
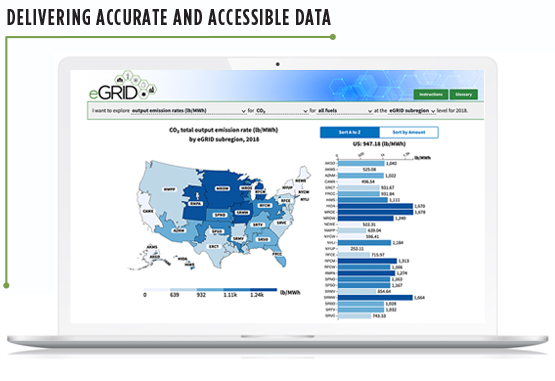
Since 2010, Abt has supported development of EPA’s Emissions & Generation Resource Integrated Database (eGRID)—the principle source of data on power generation, air pollutant emissions, and emission rates for power plants in the United States. Our latest update, released in 2020, offers the first interactive data explorer, allowing users to sort by fuel type, emission type, and region—helping to connect the dots between power generation and emission rates.
Air pollution from fossil fuel-powered electricity harms public health and leads to increased respiratory and cardiovascular illness and premature death. Calculating the public health benefits of clean energy policies can help state and local governments consider the policies’ impact and support a balanced decision-making process. Abt developed EPA's CO–Benefits Risk Assessment (COBRA) tool, a robust screening model that helps state and local governments estimate the economic value of reductions in air pollution spurred by clean energy programs, and associated public health benefits. The tool converts emissions reductions into air quality improvements and estimates adverse health impacts avoided, from asthma exacerbations and work days lost to heart attacks and deaths. COBRA then is able to monetize the benefits of avoided adverse health effects, arming stakeholders with data to improve decision making at the county, state, and national level.
Using COBRA, Abt conducted a first-of-its-kind study to determine the health impacts of RGGI (Regional Greenhouse Gas Initiative)—the U.S.’s first carbon-trading program spanning 10 Northeast states. Abt’s analysis showed that RGGI significantly reduced air pollution from fossil fuels and in just five years, resulted in a reduction in premature deaths, asthma attacks, and other benefits.
Focusing on RGGI's effects on children specifically, Abt studied prenatal and childhood exposure to air pollution and particulate matter. Results of our analysis indicated that RGGI resulted in substantial child health benefits well beyond those initially considered, including reductions in preterm births, autism, and asthma cases.

Quantifying and monetizing public health benefits of energy efficiency and renewable energy (EE/RE) is equally critical to facilitating the transition to clean energy. Using COBRA, we helped EPA develop benefit per kWh (BPK) values that estimate the monetized public health benefits of investments in EE/RE efforts across the U.S. We generated BPK values for 10 regions across the country, based on different energy scenarios and a range of economic and health assumptions. These values allow policymakers to quickly estimate the public health benefits of EE/RE policies and programs without needing to conduct extensive modeling.

Client
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA)
Projects
Emissions & Generation Resource Integrated Database (eGRID); CO-Benefits Risk Assessment (COBRA) Health Impacts Screening and Mapping Tool; Estimating the Public Health Benefit per-Kilowatt of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy
Client
Barr Foundation, Energy Foundation and the Merck Family Fund
Project
Analysis of the Public Health Impacts of the Regional Greenhouse Gas Initiative, 2009–2014
Client
Columbia University
Project
Co-Benefits to Children’s Health of the U.S. Regional Greenhouse Gas Initiative
Advancing U.N. Sustainable Development Goals
[click tab above to open]
Sector-led Capacity Building
Abt is helping countries achieve both economic growth and a more sustainable, carbon-light future through the development of nationally determined contributions to the Paris Climate Accord and sector-specific mitigation actions.
Abt worked with the governments of Azerbaijan, Kazakhstan, and Uzbekistan to reach their emissions mitigation targets. Abt also worked with each country’s stakeholders to formulate prescriptive Nationally Appropriate Mitigation Actions (NAMAs) that support the deployment of clean energy technologies. Each option was analyzed for co-benefits in terms of energy security, competitiveness, and health impacts of air quality improvements to prioritize low-carbon growth options in each country. Armed with these NAMA analyses, Abt developed investment proposals promoting agro-energy development based on renewable energy in Azerbaijan, accelerating small-scale hydropower in Uzbekistan, and fostering the use of natural gas in the transport sector in Kazakhstan. The recommendations outlined in our work illustrate the value of targeted, country- and sector-specific approaches to mitigating emissions.

In the Philippines, we led a multi-agency effort to conduct a cost-benefits and co-benefit analysis of mitigation options across six key sectors—energy, industry, agriculture, forestry, transport, and waste. The results of the study included a full sequencing of mitigation options, development of an economy-wide Marginal Abatement Cost Curve, and sector analyses. This work strengthened the Government of the Philippines’ and its partners’ capacity to plan, design, and implement low-emission development strategies and served as the evidence basis for the Philippines’ nationally determined contribution to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change.

Client
Asian Development Bank (ADB)
Project
Economics of Climate Change Mitigation in Energy and Transport in Central and West Asia
Client
U.S. Agency for International Development (USAID)
Project
Building Low Emission Alternatives to Develop Economic Resilience and Sustainability (B-LEADERS)
Advancing U.N. Sustainable Development Goals
[click tab above to open]
Supporting International and U.S.-based Partnerships to Mitigate Short-lived Climate Pollutants
Short-lived climate pollutants (SLCPs)—black carbon, methane, tropospheric ozone, and hydrofluorocarbons—account for 40 to 45 percent of global warming to date, with some more than one thousand times stronger than the global warming potential of carbon dioxide. Targeted efforts to reduce these emissions have the potential of slowing the pace of global warming by 0.6°C by 2050. Abt is working with international coalitions to unite governments, intergovernmental organizations, civil society, and the private sector in a global effort to mitigate the impact of SLCPs.
Under the auspice of the Climate and Clean Air Coalition (CCAC) and the Global Methane Initiative (GMI), Abt supports EPA's efforts to reduce SLCP emissions from the solid waste and agriculture sectors across 78 member states, including activities in China, India, Mexico, and Serbia. Since 2013, Abt’s support for EPA's CCAC and GMI activities has produced dozens of tools, workshops, and trainings resulting in thousands of hours of technical assistance, and more than 64 studies and assessments.
In the United States, Abt provides technical, communications, and outreach support for EPA’s Coalbed Methane Outreach Program (CMOP), a voluntary partnership program working with the coal mining industry to capture and recover methane as an energy source.

Reducing Refrigerant Emissions
Some refrigerants used in supermarket commercial refrigerator systems have very high levels of ozone-depleting substances and contribute to climate change at rates thousands of times higher than carbon dioxide. But retailers have options. In fact, choosing environmentally friendlier refrigerants with lower charge sizes and eliminating leaks can make a big difference in reducing harmful emissions. Over the past 13 years, our work in promoting and managing EPA’s GreenChill Partnership has aided the transition to environmentally friendly refrigerants and reductions in the amount of refrigerant used. GreenChill partners have reduced their refrigerant-contributing emission rates to almost 50 percent of the industry standard, while also significantly cutting their annual refrigerant replacement costs.
Client: U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA)
Project: GreenChill Partnership


Client
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA)
Projects
Climate & Clean Air Coalition’s (CCAC) Municipal Solid Waste Initiative; Global Methane Initiative (GMI); Coalbed Methane Outreach Program (CMOP)
Advancing U.N. Sustainable Development Goals
[click tab above to open]
Municipal Waste Management
Sustainable solid waste management is the linchpin to a livable planet. Abt has developed a suite of tools and resources that aim to scale sustainable solid waste management around the world. Partnering with EPA, Abt developed the free Solid Waste Emissions Estimation Tool (SWEET) on behalf of EPA's Climate and Clean Air Coalition’s (CCAC) Waste Initiative to calculate emissions and emissions reduction estimates at the project, source, and municipal level. The tool can be used to inform municipal solid waste management decision-making and priority setting, and allows cities to benchmark and monitor their emissions over time. SWEET has been used in 40+ cities across 30+ countries to date.
When the city of Naucalpan de Juárez, Mexico joined the CCAC’s Waste Initiative, it sought assistance improving its waste management practices. Through its partnership, the city received assistance from EPA and Abt in analyzing the environmental benefits of a planned mechanical and biological waste treatment facility using SWEET. The tool helped determine the volume of waste an anaerobic digester would divert from landfill, methane emissions avoided, and the electricity generation potential that would feed into the power grid.
In addition to the SWEET tool, Abt developed a suite of other resources for EPA to enable decision makers to gauge the potential value of projects and support emissions reduction, measurement, reporting, and verification. To help disseminate these resources to key stakeholders, we developed an online Biogas Toolkit that serves as a searchable repository to help scale sustainable projects in the biogas sectors.
Most recently, supporting EPA we developed a new global resource, Best Practices for Solid Waste Management—a comprehensive guide for decision makers in developing countries. The comprehensive document covers everything from stakeholder engagement to transportation and energy recovery, providing actionable steps to empower city-level decision makers to implement transformative decisions for their communities. We are now working with EPA to develop interactive digital learning modules to complement the guide.


Client
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA)
Projects
Climate & Clean Air Coalition’s Municipal Solid Waste Initiative; Solid Waste Emissions Estimation Tool (SWEET); Biogas Toolkit; Best Practices for Solid Waste Management: A Guide for Decision-Makers in Developing Countries
Advancing U.N. Sustainable Development Goals
[click tab above to open]

