Family Planning & Maternal & Child Health


A woman’s ability to time, space, and prevent pregnancy through safe and effective family planning methods is essential to realize gender equality, to improve women’s health, and to achieve sustainable economic development. Family planning (FP) programs that target key determinants of unintended pregnancy can prevent 32 percent of maternal deaths and nearly 10 percent of childhood deaths. Yet significant barriers—from cultural norms and social taboos to lack of access to services and information—remain for many women and girls. The result: more than 80 million unintended pregnancies and 2.7 million neonatal deaths annually. Every day, more than 800 women die from preventable causes related to pregnancy and childbirth.
Abt collaborates with governments, the private sector and civil society to help prevent unintended pregnancies, unsafe abortions, and maternal deaths by increasing demand for and access to affordable, quality FP services.
Reaching Vulnerable Populations with Messaging and Services
The United States has one of the highest teen pregnancy rates among developed nations, with persistent racial, ethnic and geographic disparities in teen birth rates. With a wide range of teen pregnancy prevention programs available, government officials need to know which programs work in different settings and with different populations. Abt undertook a replication study to test the effectiveness of three widely-used sexual risk prevention programs in the U.S., measured the effects at two time intervals, and found mixed results. While all three increased knowledge and attitudes, only the clinic-based approach reduced incidence of unprotected sex.

Project Teen Pregnancy Prevention (TPP) Replication Study
Funder U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS)

In the rural Northern and Eastern regions of Uganda, Abt is working to improve health equity by protecting poor women from large out-of-pocket payments for maternal health services. Across 35 districts, the intervention enables community volunteers to provide safe motherhood information to target populations and sell vouchers to eligible women to support healthy pregnancies and delivery. The voucher entitles a woman to receive a package of maternal health services though the accredited private health facilities without paying the service fees. The voucher package includes four antenatal care visits, services to stop mother-to-child HIV transmission, delivery with a skilled birth attendant, and referral for complications, postnatal care and postpartum family planning.
Abt also identifies and accredits private providers and reimburses them for delivery of the service package. From 2016 to 2019, 302,998 subsidized vouchers were distributed leading to 176,744 deliveries with skilled birth attendants. A rapid-cycle learning evaluation found that the activity is reaching the most vulnerable populations, with 87 percent of those purchasing the voucher unable to afford the out-of-pocket expense of the services provided.
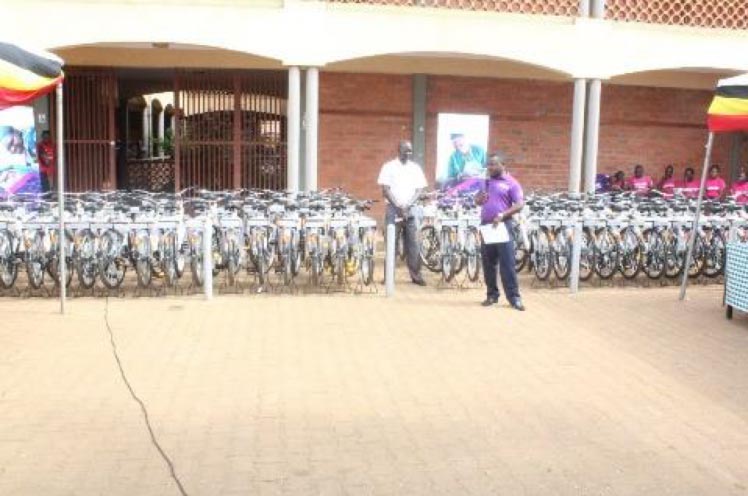

Abt and World Bicycle Relief partnered to provide 150 bicycles to enable voucher distributors to reach rural mothers who cannot be reached by paved roads, enabling them to receive medical services, from pregnancy to postnatal care.
Project Uganda Voucher Plus
Funder U.S. Agency for International Development (USAID)
Focusing on Zambia’s most vulnerable districts, communities and families, Abt worked with the Ministry of Health to scale up FP. The approach engaged all levels of Zambia’s health system: from culturally-informed community outreach to address myths and misperceptions, to supply chain support via enhanced data for decision making technology to prevent stock-outs, to supervision at district health centers, planning across provincial offices, and advocacy and stakeholder engagement at the ministerial level. Working across Zambia between 2012 and 2018, Abt helped avert an estimated 486,364 unintended pregnancies and 1,323 maternal deaths, and 120,578 unsafe abortions. Our work led to 511,174 new users of modern methods of FP, and 851,137 couple years of protection (CYP).

Project Scaling Up Family Planning (SUFP)
Funder UK Department for International Development
Crafting Culturally-Aware Engagement
Jordan has one of the fastest growing populations in the world. For a country with limited natural resources, rapid population growth presents a challenge. Even though population growth is largely due to the influx of refugees from neighboring countries, cultural factors, such as preferences for large families and traditional family planning (FP) methods prevents the country from reaching higher contraceptive prevalence rates. Abt uses innovative advocacy and engagement strategies, informed by nearly two decades of work in Jordan, to improve the policy environment for FP and reproductive health services and address socio-cultural barriers. Abt’s comprehensive national social behavior change and communication campaign used mass media, social media, point-of-service print materials, and community-based activities to reach millions of people with FP messaging.
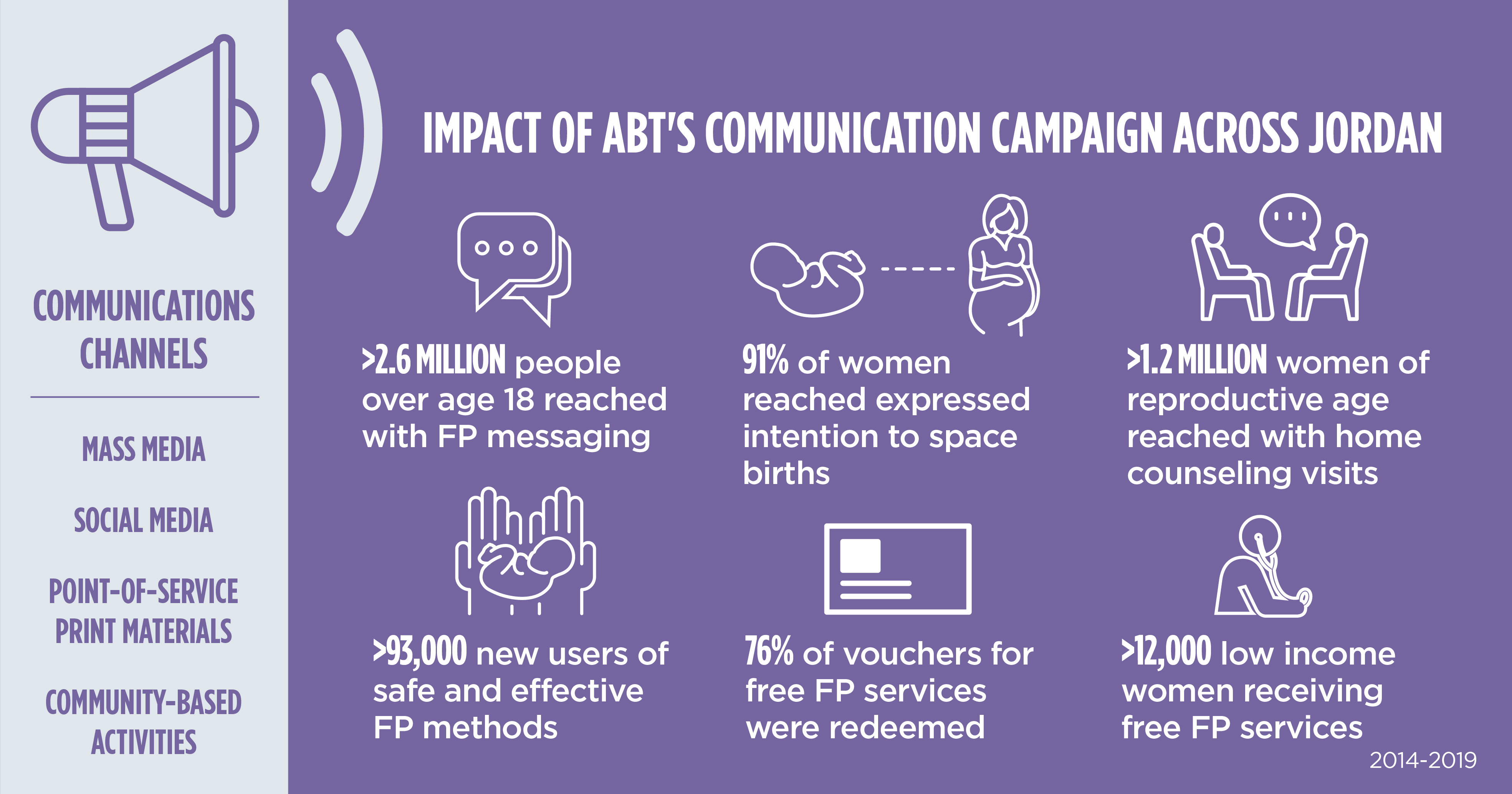
Project Jordan Communication, Advocacy and Policy Activity (J-CAP)
Funder U.S. Agency for International Development (USAID)
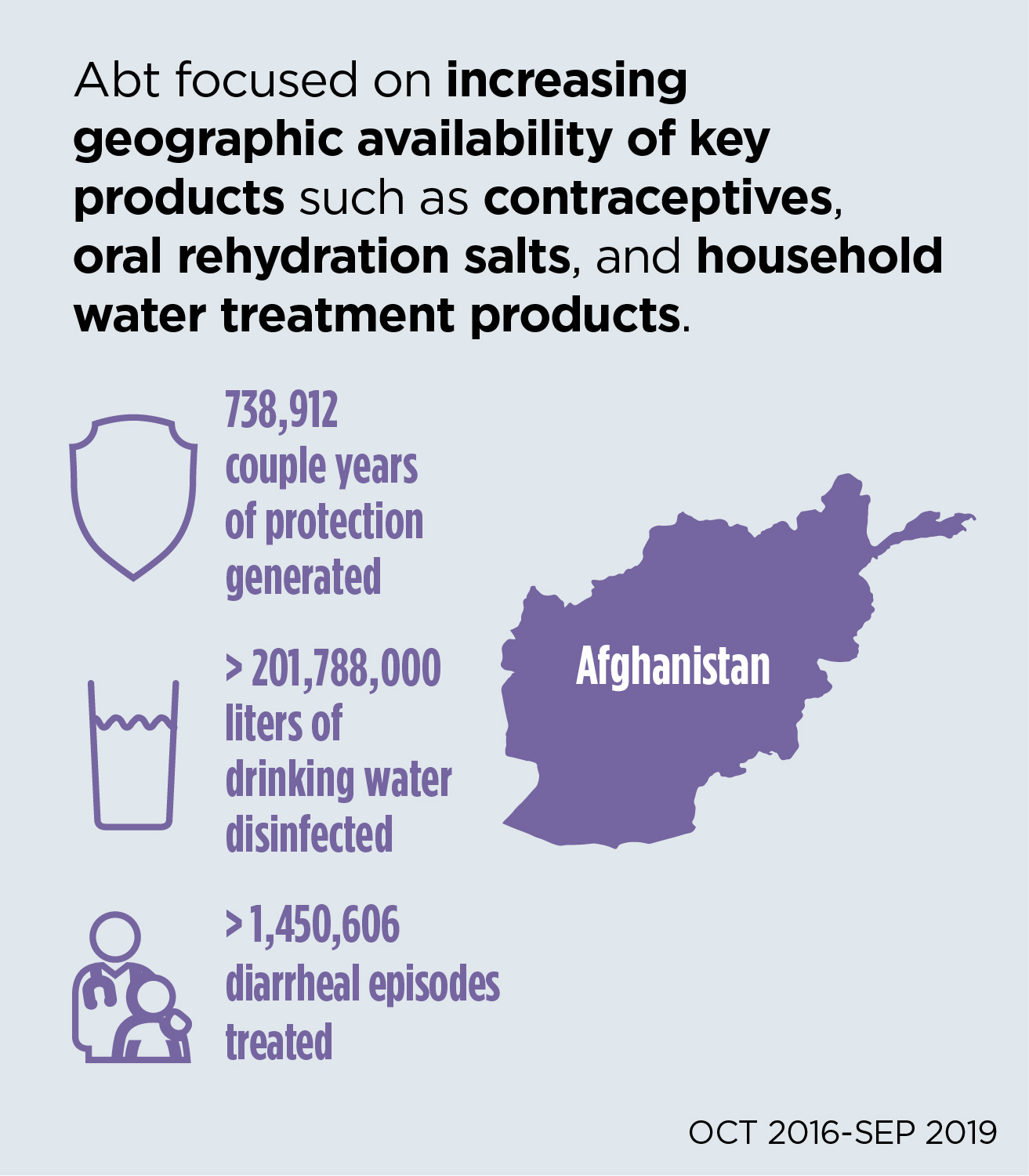
Despite recent improvements, health outcomes for women and children in Afghanistan are some of the worst in the world: 1 in every 77 live births results in the mother’s death and only 23 percent of women use modern contraception. Socio-cultural norms restrict women’s autonomy and ability to obtain health knowledge, perpetuating deeply held misconceptions. Abt focuses on strengthening the Afghan private sector in support of public sector efforts toward improved health outcomes.
Abt’s support for the Afghan Social Marketing Organization (ASMO), a leading non-governmental organization that promotes maternal and child health and FP, is scaling up the availability of products, broadcasting TV and radio campaigns to dispel myths, and catalyzing community change agents to increase women’s health knowledge.
One innovative approach: use safe, popular places such as beauty salons to encourage open dialogue and help women adopt positive health practices for themselves and their families. In one pilot, the project trained 112 beauticians to deliver information to female clients on often-stigmatized health topics. Baseline results identified a key opportunity to change FP knowledge and attitudes. The results also offer important insights for scaling up the intervention to the more than 10,000 beauty parlors in Afghanistan.

Project Sustaining Health Outcomes through the Private Sector Plus (SHOPS Plus)
Funder U.S. Agency for International Development (USAID)
Abt also is working to strengthen private sector engagement in averting unintended pregnancy and improving health outcomes across Nigeria, Haiti, Senegal, Tanzania, and Madagascar. Between October 2017 and September 2019, more than 28.6 million male condoms, 5 million oral contraceptives, and more than 3.4 million injectables were distributed through mobile outreach and social franchises, resulting in more than 1.6 million couple years of protection.
Using Data to Determine Health-Related Behavior Change Strategies

Using data to determine health-related behavior changestrategies. In India, most behavior change campaigns and public healthprograms focus on older, married couples. However, Abt’s research in India shows that young people, including married youth, have many misperceptions about reproductive health and contraception and would benefit from more accurate and youth-friendly material in an entertainment-education format.
This research helped inform a new radio series, produced by MTV and USAID’s Abt-led SHOPS Plus project, to reach the growing population of sexually active youth in India. On September 24, 2019, Abt joined MTV’s Staying Alive Foundation, USAID, and other partners to launch the new radio series. Titled MTV Nishedh Live, the series is designed to engage young people and provide them with relevant, accurate information on issues like reproductive health, peer pressure and LGBTQ stigma (Nishedh means taboo in Hindi). Each of the 15 episodes includes a young female protagonist tackling issues such as contraceptive methods and their side effects, preventing STDs and family planning, with the help of special guests such as doctors to answer questions on air. If more information is needed, the series guides audiences to the SHOPS Plus family planning helpline.
Project Sustaining Health Outcomes through the Private Sector Plus (SHOPS Plus)
Funder U.S. Agency for International Development (USAID)
Improving Quality of Care
In Zambia, USAID’s Abt-led Systems for Better Health project has focused on improving health outcomes by strengthening the systems that underpin the delivery of quality health services, and by increasing the use of high-impact health interventions at the community level. Focusing on institutionalizing quality, Abt helped the Ministry’s Provincial and District Health Offices revitalize their Quality Improvement (QI) Committees and clinical mentoring teams. The committees helped design and implement dozens of quality improvement projects in areas such as management of childhood illnesses, antiretroviral therapy retention, and increasing uptake of first antenatal visits and institutional deliveries. The percentage of facilities in 12 districts that had initiated QI projects increased from 0 in 2015 to 86 percent in 2017.
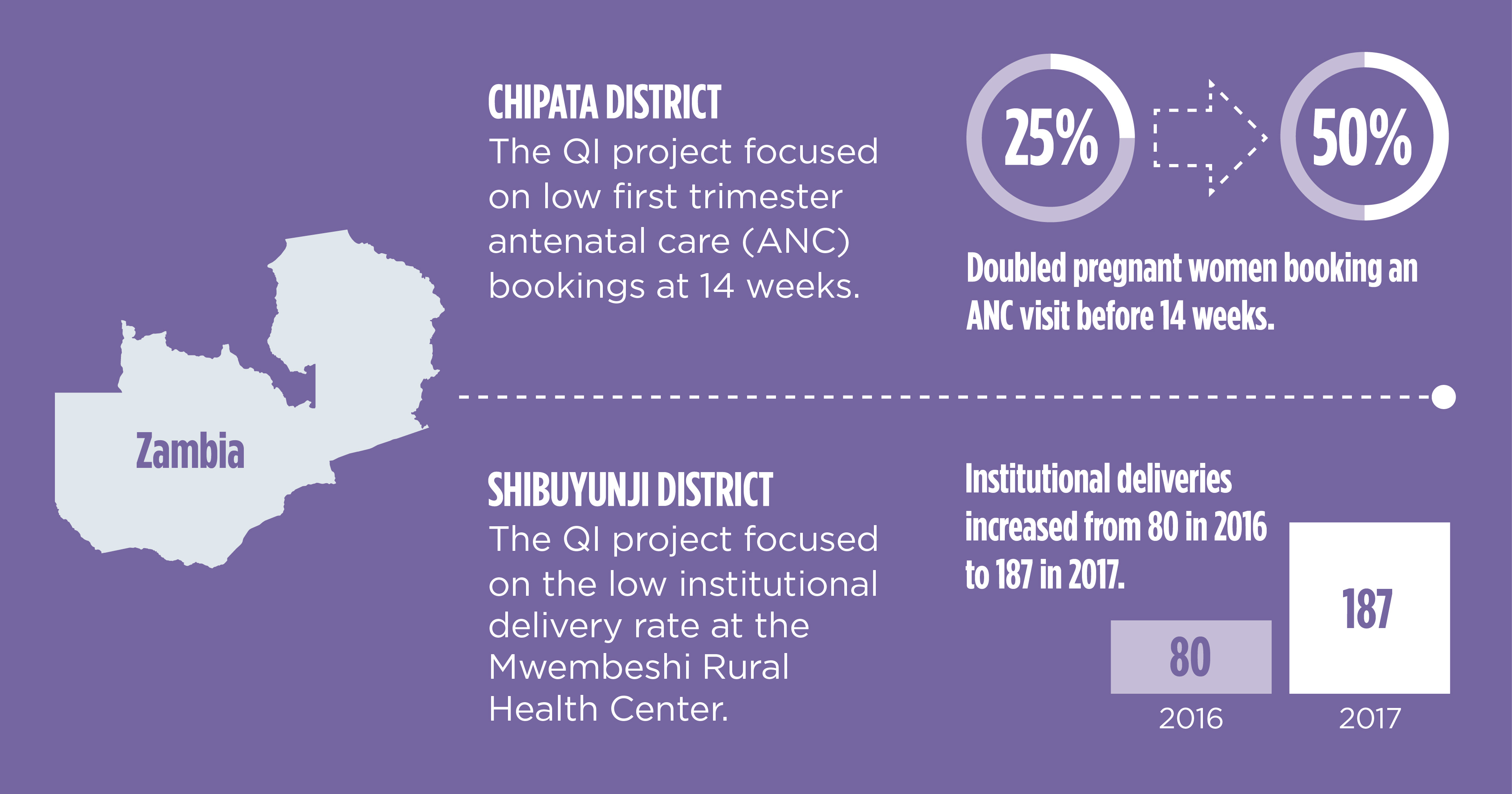
Project Systems for Better Health
Funder U.S. Agency for International Development (USAID)
Abt implements life-saving health programs in Jordan, from improving the quality of primary health care to upgrading health facilities. We collaborated with the Jordanian Ministry of Health to reduce maternal deaths from pre-eclampsia and eclampsia by standardizing clinical guidelines, increasing access to magnesium sulfate, and training providers.
To drive expansion of high-quality obstetric and neonatal health care services, Abt led major renovations of emergency, obstetrics, and neonatal departments across 14 Jordanian hospitals. Abt is continuing to enhance the availability of—and access to— integrated and high-quality services for Jordanian children and pregnant women, as well as Syrian refugees, through the Abt-led USAID Health Service Delivery project.
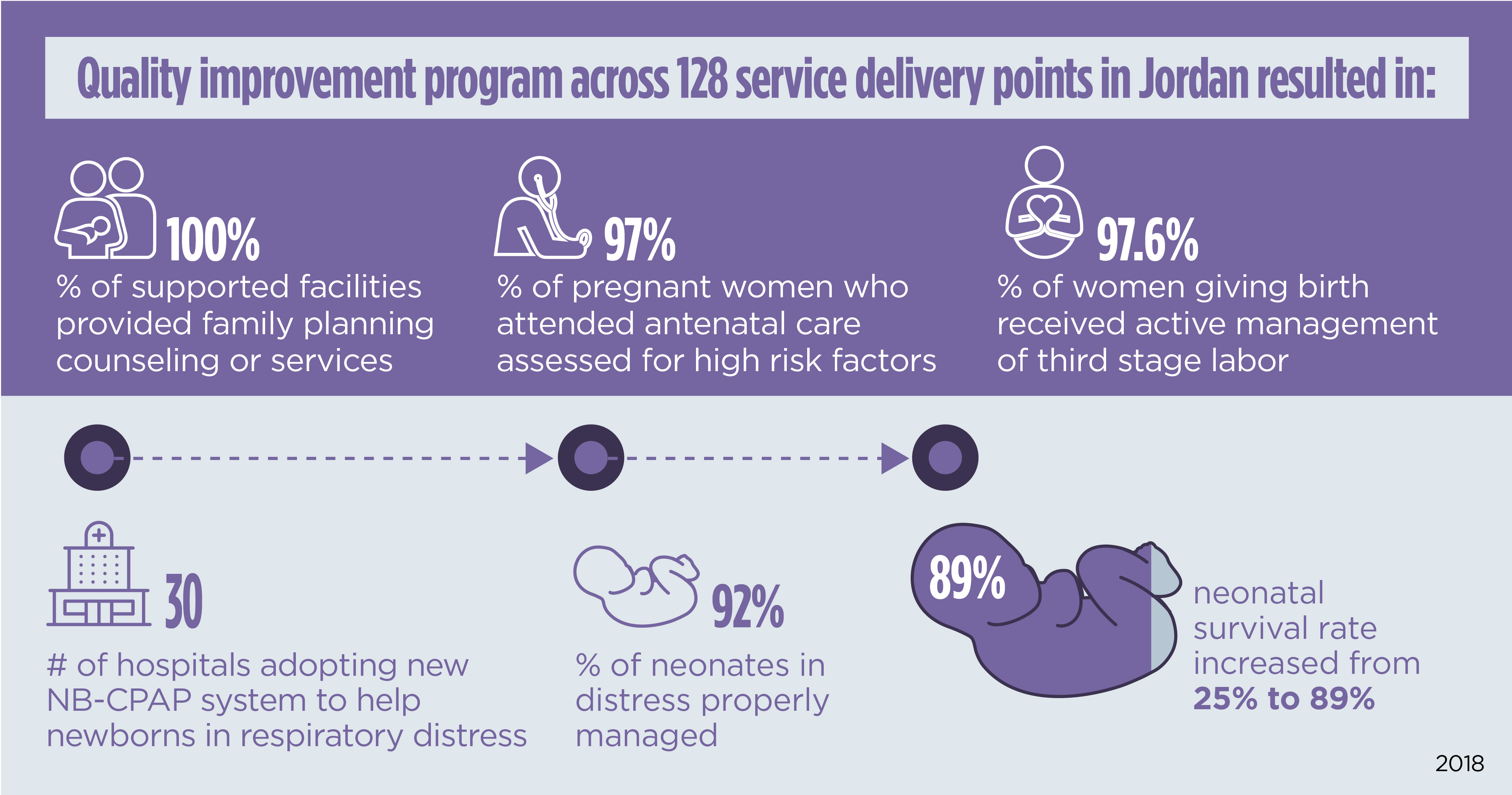
Project Health Service Delivery
Funder U.S. Agency for International Development (USAID)
Despite nearly universal deliveries in institutions with trained attendants, maternal mortality rates in the Dominican Republic in the early 2000’s remained relatively high. Focusing on 10 hospitals, Abt employed a change management approach by implementing a “Centers of Excellence” model to improve maternal and child service quality and system efficiency. This approach enabled facility staff across departments to collaborate to solve problems and initiate quality improvement, removing the barrier that “siloed” services had created in the past. One of the key results was that active management of third-stage of labor in deliveries increased from 32 to 96 percent. Actively managing third-stage labor reduces the risk of postpartum hemorrhage, one of the most common life-threatening but preventable conditions for women in labor.
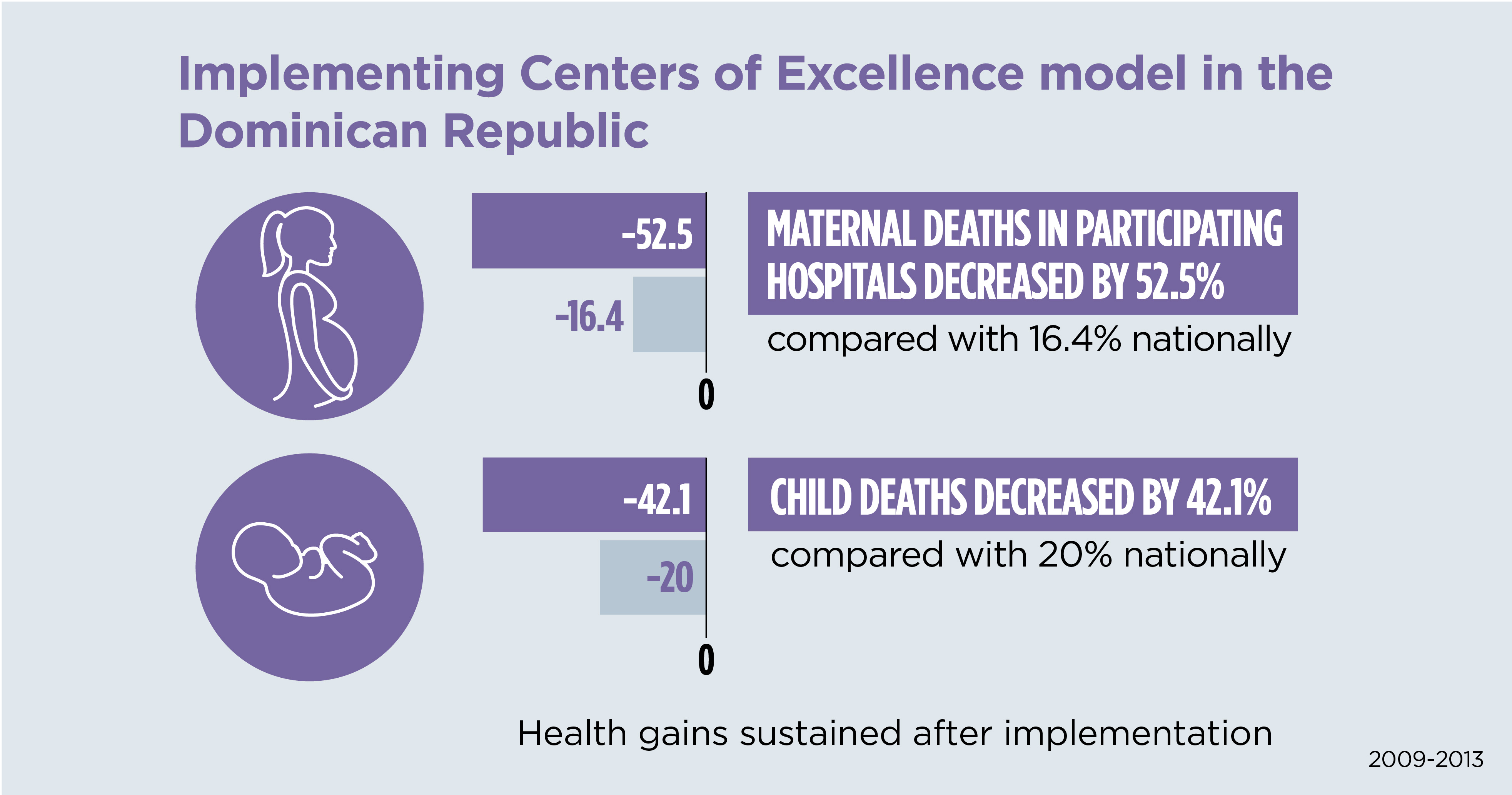
Project Maternal & Child Centers of Excellence Activity/Dominican Republic
Funder U.S. Agency for International Development (USAID)
In Mali, Abt supported the government’s goals to expand the delivery of high-quality maternal and child health services, and promote the use of services and healthy behaviors. Between 2008 and 2012, Abt saw an improvement in maternal and child health service indicators, including an increase in active management of the third stage of labor by health providers from 50 to 96.4 percent of deliveries. In addition, Abt supported innovative community-based approaches with Ministry of Health staff to reach key populations with health information. For example, we helped integrate interpersonal communication on FP into a National Nutrition Week campaign and reached 80 percent of postpartum women in the targeted pilot districts. As a direct result, the project saw a significant increase in FP uptake by new users in these pilot districts—almost doubling the number in some sub-districts.
Project Assistance Technique Nationale Plus (ATN Plus)/Mali
Funder U.S. Agency for International Development (USAID)
Although breastfeeding is the healthiest way for newborns to start their life—getting unmatched nourishment and bonding opportunities between mother and child—many hospitals in the United States lack policies and skills to promote breastfeeding. In collaboration with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Abt recruited 99 hospitals to receive technical assistance and training with the goal of attaining the Baby Friendly designation. The designation requires hospitals to adopt a 10-step approach to helping mothers start and continue breastfeeding. There’s no direct financial incentive to participate in the process, and hospitals incur significant costs to attain the Baby Friendly designation. Despite these barriers, 98 percent of the hospitals Abt recruited stayed the course, and those facilities saw a 26.79 percent jump in breastfed infants without pacifier use, and an 18.49 precent increase in skin-to skin contact after a C-section.
Project Baby Friendly Hospitals
Funder Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
Children’s Health
Though mortality among children under age 5 has declined by 58 percent since 1990, significant progress is needed to address the 15,000 daily deaths of children from largely preventable and treatable diseases, such as pneumonia, diarrhea and malaria. Vast socioeconomic and geographic disparities in child mortality persist, with most child deaths occurring in Sub-Saharan Africa, and the poorest children being more than twice as likely to die before age five as the wealthiest children. Since 2005, Abt has focused on ending such deaths by increasing awareness of effective treatment, expanding access to needed products and services, and influencing global World Health Organization guidance on life-saving interventions. We work with the public sector, private sector, and local communities to implement state-of-the-art interventions to save children’s lives.
Understanding the Burden of Childhood Illness and Care Seeking Behavior
Ending preventable child disease requires a deep understanding of caregivers’ behavior. When do caregivers choose to seek care for their sick child? Where do they go? Government facilities? Private clinics or pharmacies? What symptoms trigger caregivers to seek medical help? And how does this behavior vary with the family’s socioeconomic status? We answered these critical questions by analyzing demographic and health survey data from 24 USAID maternal and child survival priority countries, from Madagascar to Mali to Myanmar. We made the data accessible to inform policies, interventions, and programs to save children’s lives.
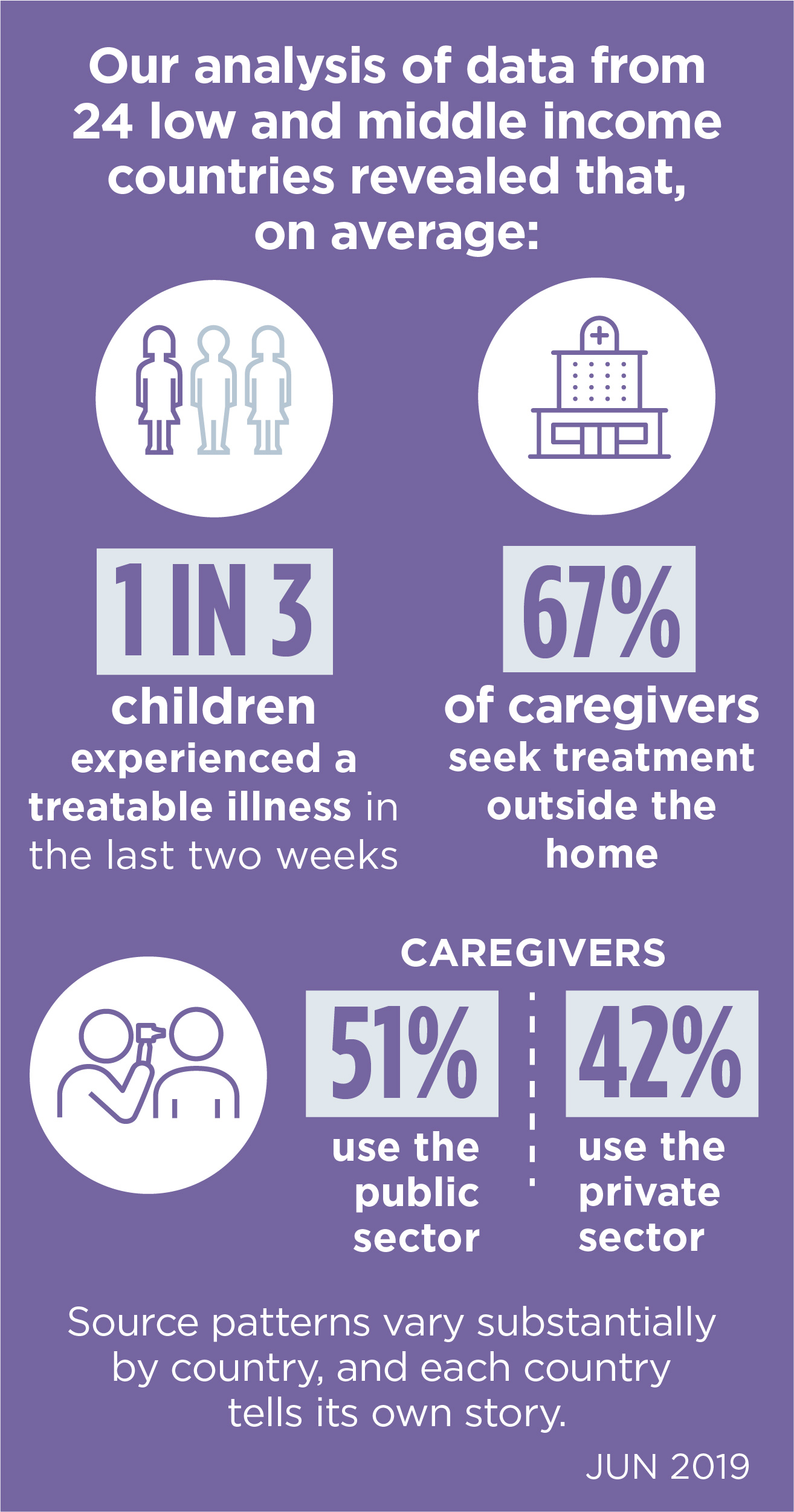
Increasing Immunizations
In Fiji, mortality among both infants and children under age 5 had remained unchanged over the five years before the Abt-led Fiji Health Sector Support Program launched, partly due to the continued burden of vaccine-preventable disease. A key challenge was the lack of immunization coverage for rotavirus and pneumococcal disease, the most common causes of both acute severe dehydrating diarrhea and pneumonia. Abt facilitated the empowerment of community-level care, improved data for decision making around vaccine coverage and effectiveness, and improved financing and procurement of new rotavirus and pneumococcal vaccines. Abt also redesigned the existing Child Health Card—which hadn’t been updated in 30 years—to include information on vaccination, healthy growth, breastfeeding, and oral health. The card was printed on a durable and waterproof non-paper material and designed to be produced at minimal cost. The innovative card was one of the 40 semi-finalists (out of over 300 entries) in the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation Records for Life Contest—a competition garnering innovations that improve child health records.
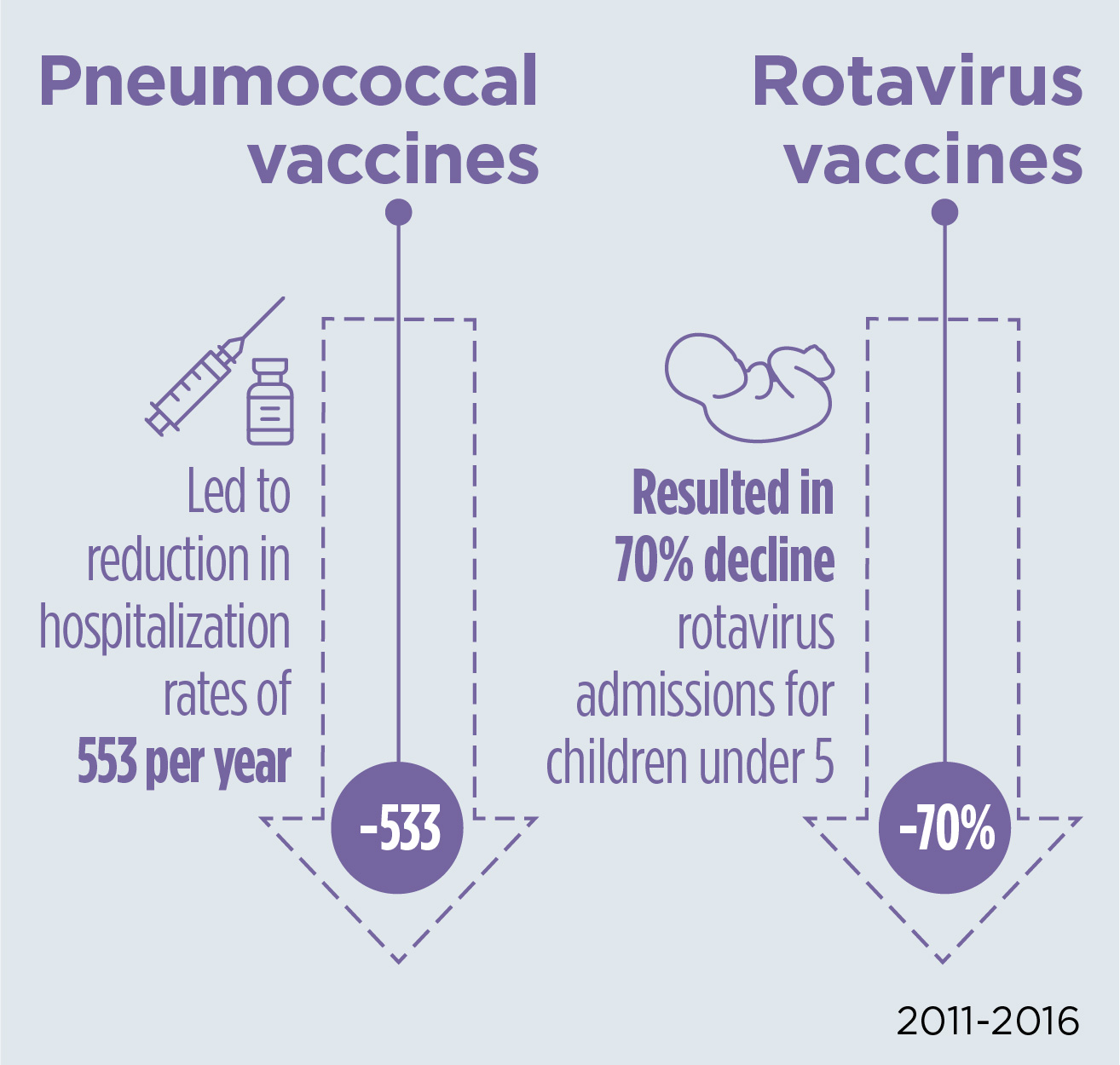
The introduction of pneumococcal vaccines is estimated to have reduced hospitalization rates by 553 per year for pneumonia, meningitis and invasive pneumococcal disease. This result, along with a 70 percent decline in rotavirus admissions for children under five, resulted in a significant reduction in the burden of providing healthcare for these diseases, freeing up limited resources for other applications.
Project Fiji Health Sector Support Program (FHSSP)
Funder Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade (DFAT), Australia
Bringing Down the Death Toll from Diarrhea
Diarrhea accounts for 8 percent of all deaths among children under 5 worldwide. Despite significant progress during the last two decades, more than 1,300 young children still die each day from diarrhea, making it a leading killer of children around the world. These deaths are preventable and are mostly related to dehydration. Children often are improperly treated with antibiotics and antiprotozoals. The most effective first-line treatments for pediatric diarrhea are oral rehydration salts (ORS) and zinc.
Between 2005 and 2015, Abt focused on improving the knowledge of effective treatments among caregivers and providers in nine countries, and ensuring affordable ORS/zinc products are available where caregivers seek care. Across the nine countries, we helped spur zinc use from zero to as high as 54 percent and helped 12 local manufacturers introduce high-quality, affordable zinc products to the market, providing more than 19 million treatments of ORS and zinc through private sector channels.
Project Social Marketing Plus for Diarrheal Disease Control (POUZN) and Sustaining Health Outcomes through the Private Sector (SHOPS)
Funder U.S. Agency for International Development (USAID)
Our efforts to advance awareness of ORS/zinc effectiveness continue today. For example, in Nepal, where diarrhea is one of the most common illnesses among children and continues to be a major cause of mortality and morbidity, Abt is helping a local social marketing organization strengthen its child health program and launch an ORS/zinc co-pack product. Our qualitative research uncovered key insight to better understand diarrhea care seeking and treatment perceptions and practices, which will help guide forthcoming community-based demand creation activities.

Project Sustaining Health Outcomes through the Private Sector Plus (SHOPS Plus)
Funder U.S. Agency for International Development (USAID)
In Ghana, Abt began a diarrhea management program in 2012. A key innovation was to engage local pharmaceutical firms to produce and market locally ORS and zinc products. Abt helped local manufacturers with brand promotion, distribution logistics in rural communities, and quality assurance via partnerships with U.S.-based drug standards organizations. To ensure proper administration of ORS/zinc, we trained Ghanaian health providers on diarrhea management. To catalyze demand, we conducted mass media campaigns to raise caregiver awareness.
Abt’s work in Ghana continues to scale. Since 2015, Abt has trained 11,671 health professionals in child health management and treatment, including malaria and diarrhea. Continuing to work closely with local manufacturers, Abt distributed a total of 95,802,166 zinc tablets, including 23,478 co-packs of ORS and zinc for diarrhea treatment to date.
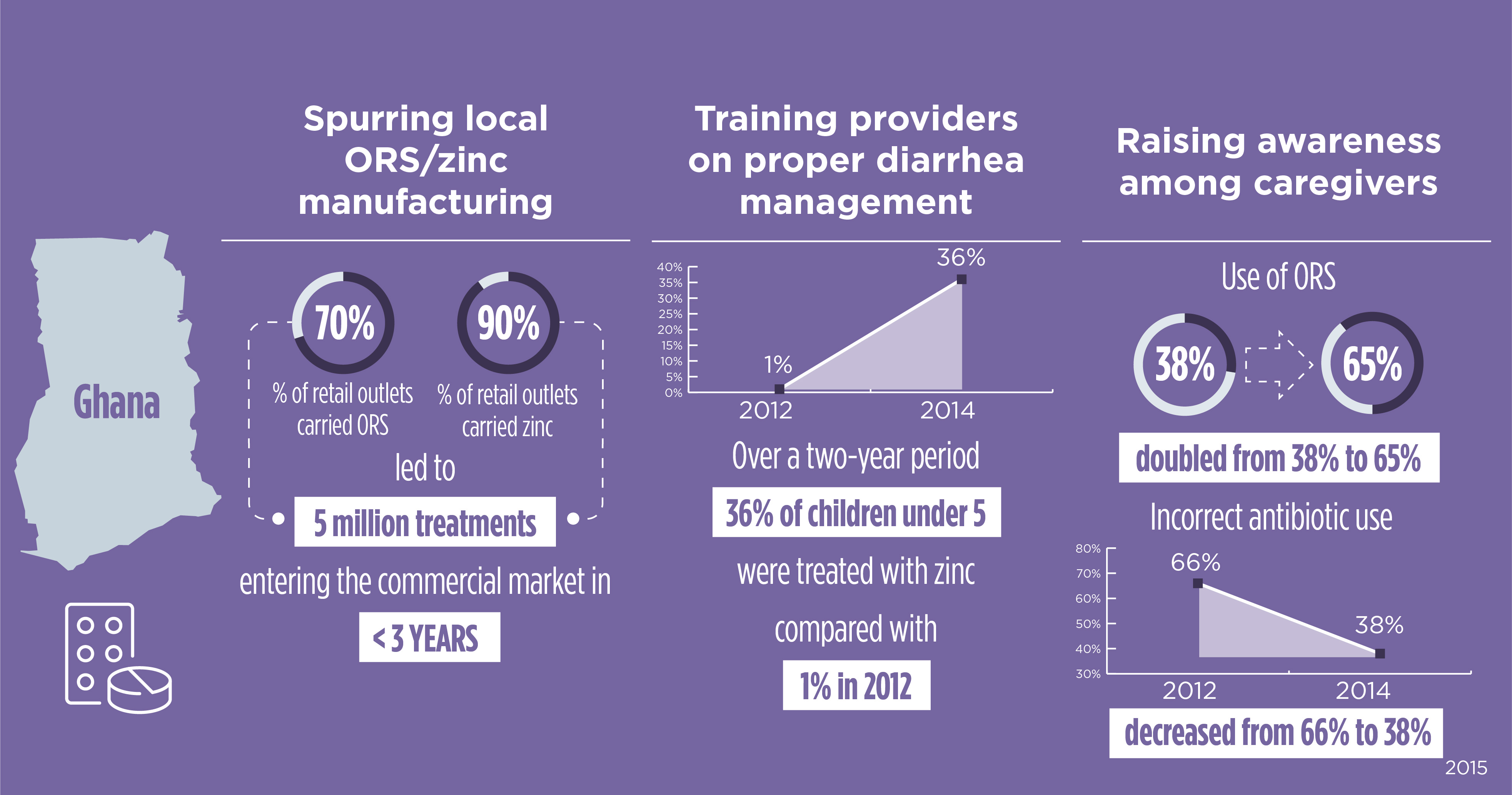
Project Sustaining Health Outcomes through the Private Sector (SHOPS), and Sustaining Health Outcomes through the Private Sector Plus (SHOPS Plus) Ghana
Funder U.S. Agency for International Development (USAID)
In Afghanistan and Madagascar, we focus on increasing access to products via private sector engagement and by building awareness through social and behavior change communication campaigns. Since 2015, Abt has directly supported the treatment of nearly 1.2 million cases of childhood diarrhea with ORS, zinc, and ORS/zinc co-packs.
Project Sustaining Health Outcomes through the Private Sector (SHOPS), and Sustaining Health Outcomes through the Private Sector Plus (SHOPS Plus) Ghana
Funder U.S. Agency for International Development (USAID)
Abt worked with partners to facilitate the World Health Organization’s 2019 landmark decision to include a new listing of co-packaged ORS and zinc on its Model List of Essential Medicines for Children.

Abt worked with partners to facilitate the World Health Organization’s 2019 landmark decision to include a new listing of co-packaged ORS and zinc on its Model List of Essential Medicines for Children.
