Non-Communicable Diseases


Reducing the global burden of non-communicable diseases (NCDs) is an urgent imperative, as conditions such as heart disease, stroke, cancer and diabetes are collectively responsible for nearly 70 percent of deaths worldwide.
Working with governments and foundations around the world, Abt evaluates programs, provides technical assistance, and advises on policies to help communities and individuals detect, manage and prevent these ubiquitous illnesses.
Expanding Access to Care
Partnering with the Medtronic Foundation, Abt led a global effort, HealthRise, to expand access to care for cardiovascular disease and diabetes among underserved populations in Brazil, India, South Africa and the United States.
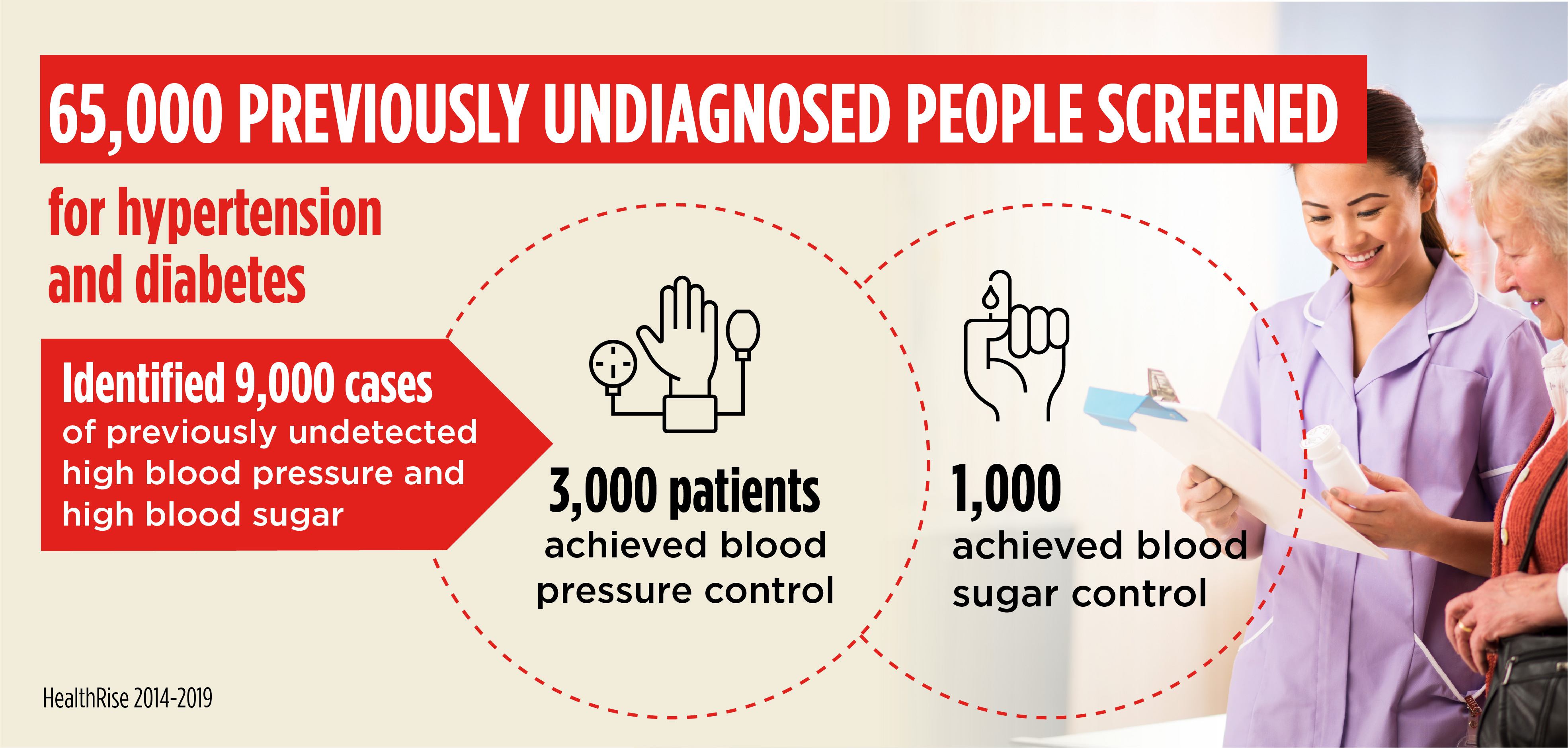
In the U.S. state of Minnesota, nearly half the population has diabetes or is at risk for the disease, with minorities, people with low incomes and the elderly disproportionately affected. Among those with diabetes, 31 percent also have heart disease, the second leading cause of death in the state.
HealthRise interventions focused on strengthening healthcare delivery in the community, extending care from the clinic into patients’ homes and providing a holistic response to patient needs and barriers.
One innovation was integrating nonclinical staff into patients’ care teams to deepen understanding of social and cultural norms. This empowered patients to self-manage their chronic disease. Optimizing use of electronic medical records and using educational text message tools to increase patient participation in nutrition, health and wellness activities also contributed to the success of this program.


In Brazil, despite steady progress since 2000, 74 percent of all deaths are still attributed to NCDs. The Abt-led HealthRise program focused on NCD screening through health fairs and at-home services, increasing referrals to primary care centers and clinics and ensuring treatment continuity. By facilitating patient empowerment, improving care coordination, and transitioning clinics from paper to Brazil’s web-based medical records system, HealthRise delivered significant improvements in NCD care and patients’ health outcomes.
Project HealthRise
Funder Medtronic Foundation
In Jordan, Abt supported a number of interventions to improve the quality of care for patients with hypertension and diabetes at the primary healthcare level. To support the use of NCD-related data for decision making, Abt introduced an NCD information system and helped 120 health centers to collect and analyze data on hypertension and diabetes screening and management. Over five years, the percentage of controlled diabetic patients at these facilities increased from 42 percent to 54 percent.
Working with the government of Jordan, Abt supported the development of a national policy for diabetes testing at health centers, and, working with stakeholders on the ground, initiated critical partnerships to strengthen and expand the scope of services offered. These included NCD screening and referral, as well as other critical services such as nutrition counseling and gender-based violence counseling. These partnerships strengthened the health system’s ability to respond to the increasing demand for health services by Jordanians and Syrian refugees.

Project Health Systems Strengthening II (HSS II) and Jordan Health Service Delivery (HSD) Activity
Funder United States Agency for International Development (USAID)
In Fiji, diabetes and its complications are the top causes of death and disability, and they are on the rise. A big challenge is that many cases go undiagnosed, meaning that many people are accessing healthcare services at a late stage when conditions are much harder and more expensive to manage. This results in poorer health outcomes and higher healthcare costs.

Partnering with the Ministry of Health, Abt focused on diabetes prevention and early intervention. Abt helped develop systematic population-level screening of adults 30yrs+, and tools promoting primary prevention, referrals for diagnostic testing and early interventions. To meet the anticipated increase in demand for services, Abt facilitated the upgrade of specialist outpatient departments (SOPDs) at two major hospitals and developed the minimum standards of NCD care at the SOPDs to improve quality.
Zeroing in on the increasing rates of leg amputations, Abt’s situational analysis uncovered minimal preventative foot screening for diabetic patients, but importantly identified key local champions within the nursing cadre to drive the ‘inspect and protect’ approach funded and assisted by Abt. This approach included a foot care training manual, referral pathway flow chart, educational materials and monofilaments for foot assessments, leading to a drastic decline in amputations.
Project Fiji Health Sector Support Program (FHSSP)
Funder Australian Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade (DFAT)
Driving Healthy Behaviors
Risk factors for NCDs are modifiable—that’s why efforts to change behaviors through incentives and awareness building are key to stave off the disease.
Informing Policy
In the Caribbean, Abt’s health expenditure tracking in Barbados and Dominica revealed limited spending on preventive care for NCDs, which account for more than 75 percent of deaths. Using evidence generated from the analysis, both islands have introduced a tax on sugar-sweetened beverages (SSBs) to pay for increased government spending for prevention and to help address the rising rates of NCDs. Because unhealthy diets, and SSBs specifically, are associated with Type 2 diabetes, obesity, and cardiovascular risk factors, taxing SSBs is a World Health Organization recommended population-level effort to tackle these diseases. The 10 percent tax on SSBs in Barbados not only generated additional funding for the health sector, but led to a decrease in sales of SSBs in major grocery chains.
Project Health Finance and Governance (HFG)
Funder United States Agency for International Development (USAID)
Building Awareness to Manage Disease
Empowering people through improved knowledge of risk factors and detection is critical to addressing NCDs like diabetes. Partnering with ideas42, Abt designed, implemented and evaluated behaviorally optimized Google health cards on Prediabetes and Diabetes for the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). When the program was being promoted, the cards appeared in online searches of relevant terms to incent users curious about these conditions to learn more. Once on the Health Cards page, users could take an online risk test and seek information about the National Diabetes Prevention Program.
Abt’s evaluation of CDC’s original landing pages found sharp increases in risk test traffic and engagement since the new health cards were implemented.
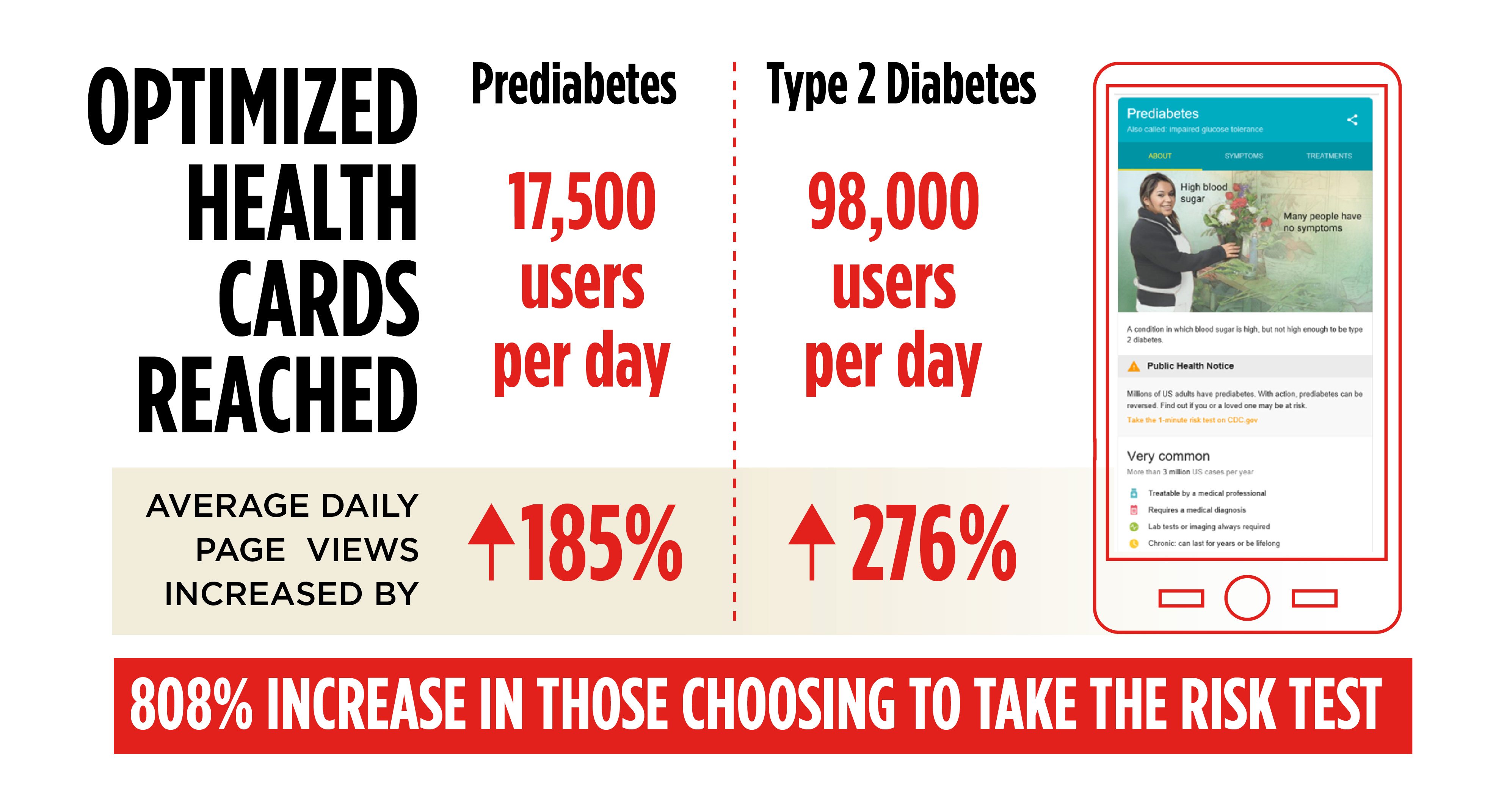
Project Building a Behaviorally-Optimized Health Card for Type 2 Diabetes Prevention and the National Diabetes Prevention Program
Funder Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
Turning Data into Insight
From population-level data to state-of-the-art surveys capturing experiences of key populations—Abt’s data capture and analytics capabilities help turn data into insight.
Generating Standardized, High-Quality Data
Consistent population-level data on risk behaviors and preventive health practices related to NCDs can offer critical insight—yet data is only as useful as it is standardized, comprehensive and accessible. In the United States, the Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System (BRFSS) provides consistent data to identify trends, track benchmarks and implement solutions at national, state and local scales. The BRFSS includes critical data standardization processes and is implemented through state-based telephone surveys, with oversight and assistance from the CDC.
Abt provides critical support to the BRFSS, ensuring public health departments collect the high quality data they need to improve programs and services. Abt’s support includes advancing statistical methods, questionnaire development, creation of public-use data files and reports, building dashboards and web query tools and conducting point-in-time surveys on topics such as asthma, tobacco and child health.
The high quality data that we have collected has been used to demonstrate that:
-
Over half of rural adults with arthritis have an arthritis-attributable activity limitation
-
Transgender adults are significantly more likely to be uninsured
-
Increasing physical activity and reducing smoking could provide adults with depression a higher life expectancy and quality-adjusted life expectancy
Surveying Women
NCDs are the number one killer of women around the world and affect women disproportionately. NCDs also often impact women in unique ways—and yet data on women’s views and experiences were limited and therefore under-represented in policy and health interventions. To address this gap in knowledge, Abt and partners launched a global survey of 10,000 women to assess their perceptions and experiences with NCDs. The effort included survey design, data collection and analysis, and generated important insights to draw attention to the impact of NCDs on women’s lives around the world.
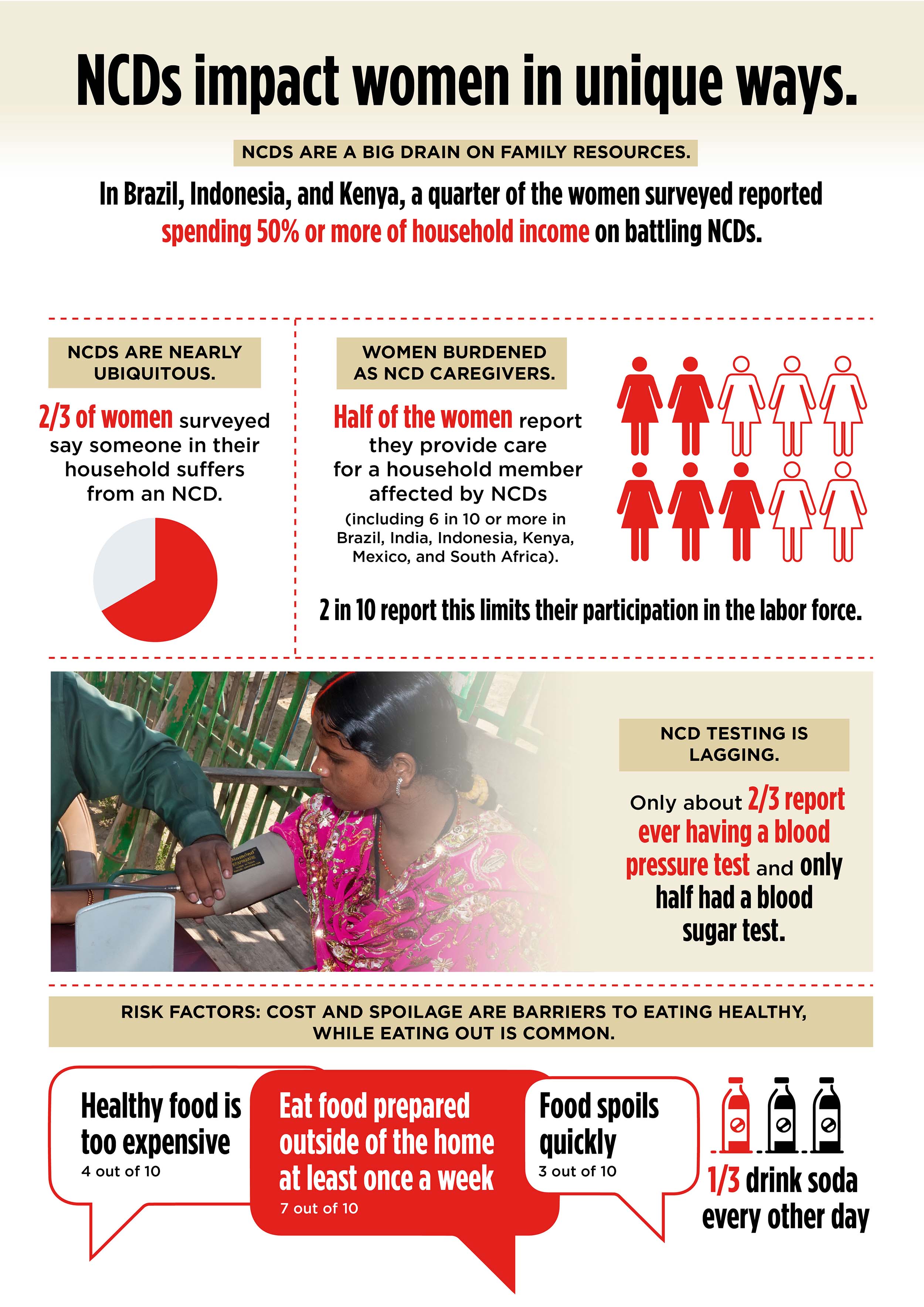
Project Women’s Voices on NCDs
Funder Arogya World
