Climate Adaptation & Resilience
Communities around the world are already living with the effects of a rapidly changing climate. Swiftly reacting to that change—and proactively investing in resilience—is the key to saving lives and livelihoods. From helping communities and countries understand the impacts and risk, to equipping them to deal with climate change, Abt is strengthening adaptation and resilience planning around the world.
Understanding Impacts and Risks
A prerequisite for effective adaptation and resilience planning is understanding climate risks. Abt’s work has spanned regions and risks from coastal flooding in the Caribbean to winter recreation in the U.S.—delivering model climate impact projections based on scientific data and economic analyses.
Most Caribbean and Latin American countries, have coastlines that are vulnerable to sea level rise and inland areas where extreme precipitation events can cause flooding. The Inter-American Development Bank asked Abt to develop projections for the years 2040 and 2070, with a focus on the transport sector. We created 26 country-specific climate change projections using dozens of general circulation models, which represent biophysical processes to simulate atmospheric and oceanic responses to increasing greenhouse gas emissions. We ran geospatial analyses and prepared a series of maps, guides, and tools for each of the 26 countries to advance adaptation planning.
Focusing on the United States, we conducted a meta-analysis of scientific and economic literature that forecasts the impacts of climate change on future economic damages from hurricanes and cyclones. The result was the first quantitative approach to develop a range of projected economic damage costs from extreme weather events in the United States. Our approach was presented at the American Geophysical Union Annual Meeting and has since been published in the peer-reviewed journal Climatic Change. This approach can also be used for projecting costs of economic damages from other extreme events across the United States.
Robust Indicators
As the climate changes, physical manifestations are all around us, from hotter summers and earlier bloom dates, to increasing ocean acidity. The effects are broad, and having robust indicators to enable measurement is critical. Our team supports the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency’s (EPA) Climate Change Indicators compilation, directly developing five of these indicators related to incidence of Lyme disease and West Nile virus, wildfires, temperature trends, and heat-related deaths.


Recreational Activities
Climate change has implications for every aspect of our lives, including across cherished recreational activities.
Freshwater fishing is an important activity that contributes significantly to local economies in many parts of the country. Climate change threatens to disrupt these habitats and affect certain fish populations—such coldwater fish like trout and salmon—that are least tolerant to higher stream temperatures and changes in river flow. Abt projects that by 2090, coldwater fishing days could decline nationally by more than 90 million days per year due to unsuitable habitats, with a lost cumulative recreational fishing value of up to $45 billion (2015$) by 2090.

Climate change also threatens winter recreational activities and will have important implications in areas where these industries are a substantial part of the region’s economy. Abt conducted a study estimating the impact of climate change on downhill skiing and snowboarding, cross-country skiing, and snowmobiling at 247 sites across the contiguous U.S. While improvements in snowmaking technology can offset declines in natural snowfall for downhill skiing, these adaptive responses are less effective for cross‐country skiing and snowmobiling. Abt estimates that season length changes could result in tens of millions of foregone recreational visits annually by 2090, with an annual monetized impact of hundreds of millions of dollars.

Client
Inter-American Development Bank (IDB)
Project
Transport and Climate Change Adaptation in Latin America and the Caribbean
Client
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA)
Projects
Meta-Analysis of Literature on the Cost of Climate Extremes; Climate Change Indicators; Climate Change Impacts and Risks Analysis (CIRA); Effects of Climate Change on Winter Recreation
Advancing U.N. Sustainable Development Goals
[click tab above to open]
Equipping Communities to Respond to Climate Change
In the United States, Abt has shaped housing and community revitalization practices and policy for more than 50 years. As climate change exacerbates risks to housing—and to low- and moderate-income residents in particular—it is critical to integrate resilience planning into housing-related social programs. With this goal in mind, Abt partnered with the U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD) to develop the Community Resilience Toolkit. The Toolkit is organized using a clear and concise format that communities can use to identify both potential vulnerabilities from climate hazards, such as wildfires or coastal storms, and the specific actions they can take to reduce their vulnerabilities. Actions are summarized in four categories: planning, buildings and infrastructure, environment, and people. Importantly, the toolkit also provides guidance on how to use HUD funds and other innovative financing options for needed resilience and adaptation strategies.

Cooling Urban Environments
Urbanized areas experience higher temperatures than outlying areas, exacerbating incrementally increasing temperatures and periods of extreme heat. These “heat islands” experience daytime temperatures up to 7°F higher than outlying areas on average. To increase public awareness around the topic and arm communities with actionable solutions, we launched Cool Your Community as part of EPA’s Heat Island Reduction Program. Cool Your Community is a social media toolkit in English and Spanish geared to mobilize individuals and communities to cool the local environment. Since 2019 the Program’s offerings, including web content, newsletters, and webinars, have reached more than half a million people.
Flood Risk and Hurricanes
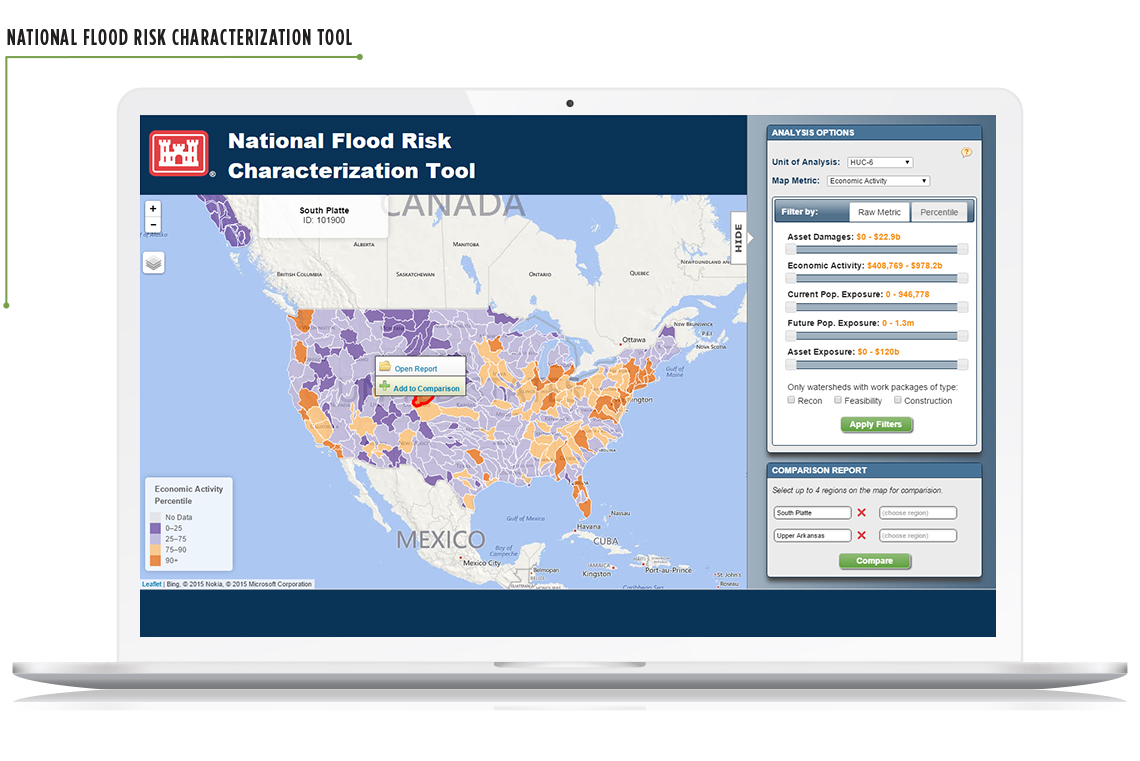
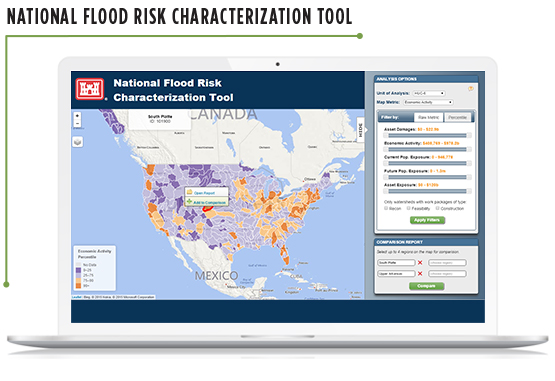
Most hurricane and cyclone damage is caused by water, not wind, and the number of hurricanes making landfall in the U.S. is growing. Climate change has increased flood risks in both coastal and inland areas. To assess flood risks and establish priorities for the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers across the United States, Abt designed and developed the National Flood Risk Characterization Tool. The tool assesses relative risks based on the potential for asset damages, human exposure, and exposure of emergency response infrastructure, along with other vulnerability metrics. Through the tool’s map-based interface, decision makers can easily visualize what may confront them and make informed decisions on spending priorities. Zeroing in on state and local needs, Abt developed an inland flood toolkit for the state of New York (.pdf) to enable communities to assess their current and future inland flood risks, including flood frequency and magnitude.
Hurricane Relief
With signs that more intense hurricanes will become the norm in the coming years, heeding lessons from previous recovery efforts can lead to stronger responses in the future. Community Development Block Grants (CDBG) are a key mechanism in the U.S. government’s disaster recovery response for affected areas.
In Louisiana and Mississippi post Hurricanes Katrina and Rita, Abt analyzed use of CDBG funds in housing recovery efforts by studying FEMA (Federal Emergency Management Agency) damage assessments and state program data as well as on-site observations. We found that many CDBG recipients’ rebuilding and repair costs far exceeded total funds available from insurance, CDBG grants, and other sources of recovery funding. The data indicated that the grants did not always result in their goal of a rebuilt home for a family; barriers to rebuilding included insufficient financial resources and contractor fraud.
Bringing our expertise in the CDBG program to the U.S. Virgin Islands and Puerto Rico, Abt is helping local officials recovering from Hurricanes Maria and Irma assess and measure unmet needs, navigate CDBG program rules and regulations, and design and coordinate recovery activities across housing, economic development, and infrastructure.


Disaster recovery can also provide an opportunity to rethink old paradigms. Following Hurricane Harvey’s destructive tear through Houston, Texas, city and community leaders saw rebuilding as an opportunity to advance fair housing strategies. Abt is helping the city design recovery programs and strategies that promote equity and address historically persistent barriers to fair housing. We are working to ensure that the resulting strategies are incorporated into key planning documents as well as the city’s use of CDBG funds and other federal affordable housing grants.
After Hurricane Sandy devastated the U.S. Atlantic Coast, the Hurricane Sandy Coastal Resiliency Program—administered through both the U.S. Department of Interior (DOI) and the National Fish and Wildlife Foundation (NFWF)—invested more than $302 million to support 160 projects designed to improve the resilience of ecosystems and communities to coastal storms and sea level rise. NFWF and DOI commissioned Abt to evaluate effectiveness of the program and advance understanding of coastal resilience strategies—including restoring marshes, constructing living shorelines, improving aquatic connectivity, restoring beaches and dunes, supporting coastal resilience planning, and conducting coastal resilience science. Our analysis concluded that the program has significantly improved ecological and community resilience throughout the region. Abt also developed an innovative approach for understanding the long-term socioeconomic impacts of specific restoration projects.

Public Safety & Disaster Response Competency
In 2019, Abt achieved Amazon Web Services (AWS) Public Safety & Disaster Response Competency status. This differentiates Abt as an AWS Partner Network member that provides demonstrated technical proficiency and proven customer success with implementing work focused on Disaster & Public Safety Data and Analytics Tools and on Disaster & Public Safety Infrastructure Recovery Tools. The designation attests to Abt’s expertise in helping national and local leaders develop resilience by modelling all the sectors impacted by disaster, including transportation, health, housing, and energy. AWS provides Abt the tools and services to deliver precise predictive models and decision tools for decision makers at all levels.


Client
U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD)
Projects
Community Resilience Toolkit; Community Development Block Grant – Disaster Recovery (CDBG-DR) Certification and Action Planning; CDBG Disaster Recovery Assistance; Hurricane Harvey - Fair Housing
Client
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA)
Project
Heat Island Reduction Program
Client
U.S. Army Corps of Engineers
Project
National Flood Risk Characterization Tool (NFRC)
Client
New York State Energy Research and Development Authority (NYSERDA)
Project
Inland Flood Risk Toolkit
Client
U.S. Department of Interior (DOI)
Project
Evaluation of Hurricane Sandy Coastal Resilience Program
Advancing U.N. Sustainable Development Goals
[click tab above to open]
Strengthening National Adaptation and Resilience Planning Around the World
Governments around the world are seeking to develop comprehensive adaptation strategies to weather the effects of a changing climate and enhance resilience to what is yet to come.
Engaging the Private Sector in India
In India, Abt partnered with the United Nations Development Programme and three municipalities to design 10 public-private partnerships (PPPs) for disaster risk reduction in the eastern cities of Visakhapatnam, Vijayawada, and Cuttack—which have a combined population of almost 5 million people—to reduce disaster risks related to cyclones, monsoon flooding, and extreme heat and precipitation events. The PPPs draw on both the technical expertise and financing from the private sector to improve coordination of disaster response in public health systems, strengthen community resilience, mitigate impacts of urban heat islands, and improve solid waste management to increase storm water drainage during heavy rains and flooding.

Client: U.S. Agency for International Development (USAID)
Project: Climate Economic Analysis for Development, Investment and Resilience (CEADIR)
Working with the Central Asian Republics, we developed a comprehensive adaptation training portfolio with an emphasis on adaptation financing. Our team conducted more than a dozen national and regional training workshops, and fostered a meaningful dialogue among the five Central Asian Republics and the U.S. Agency for International Development (USAID) on adaptation and best practices.
In Kazakhstan, we revised the country’s Environmental Code to integrate climate change into sector planning, in addition to providing technical support for each country’s development of a National Adaptation Plan.
Through deeper engagement in Tajikistan, we integrated climate risk and resilience into urban development planning through
trainings, development of local resilience action plans and climate risk-screening tools, and the development of a state-of-the-art
climate modeling facility. These actions significantly increased resilience of the Tajik people, including reducing the number of people affected by drought and floods by 20 percent and losses from drought and floods by 25 percent.

In Peru, Senegal, and Madagascar, Abt developed adaptation finance trainings to support each country’s adaptation planning and National Adaptation Plan development. In Peru, we prepared sectoral adaptation portfolios for agriculture, health, and fisheries and aquaculture. In Madagascar, our teams trained stakeholders to integrate climate considerations into their biodiversity plan. In Senegal, we trained fisheries and agriculture sector stakeholders in setting adaptation objectives, developing priority adaptation actions, and assessing climate finance readiness. Abt shared lessons learned across adaptation planning work in these countries through four National Adaptation Plan Global Network events and nine other knowledge exchange platforms.

Focusing on the power sector in Laos, we conducted a stakeholder-driven vulnerability assessment and developed a resilience action plan to address the highest risks. Participants in the stakeholder engagement process concluded that extreme precipitation, extreme temperatures, flooding, and landslides pose the greatest risk to the sector. These risks and select resilience actions were incorporated into the country’s Integrated Resource and Resilience Plan.
USAID Climate Risk Management Assessment
The adverse impacts of climate change threaten to roll back decades of progress toward improving economic security in vulnerable countries through U.S. development assistance. In 2016, USAID implemented a policy requiring all agency projects and activities to integrate climate risk management (CRM) into their design and implementation. Abt is partnering with USAID to advance the Agency’s Mission staff’s understanding of the benefits of integrating CRM into programming through project-level case studies and blogs. Abt is working with seven Missions to determine and monetize CRM benefits to high-profile USAID projects in health, agriculture, water management, fisheries, and conflict.

Client: U.S. Agency for International Development (USAID)
Project: Climate Integration Support Facility (CISF)

Client
U.S. Agency for International Development (USAID)
Projects
C5+1 Adaptation; Climate Economic Analysis for Development, Investment and Resilience (CEADIR); Clean Power Asia
Client
Asian Development Bank
Project
Building Capacity for Climate Resilience in Tajikistan
Advancing U.N. Sustainable Development Goals
[click tab above to open]
